Background
Naive Bayes is based on Bayes’ Rule which finds the probability of an event occuring given the probability of another even that has already occured. It is based on prior probability. We calculate the conditional probability of each term in the dataset.
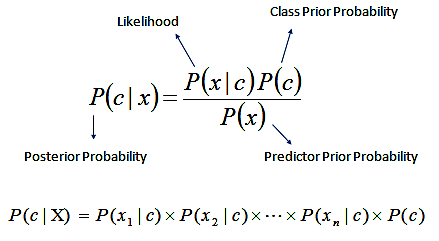
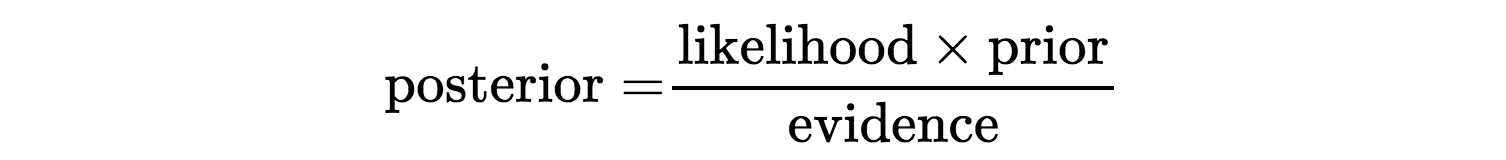
General Idea
I use the prime_genre column of the dataset to categorize the app which includes categories like “Entertainment”,“Education”,“Productivity”,etc. This serves as a type of Ground Truth since the classifier will base it assumption on words that were used in the description of these rows to predict what type of app the query is. I preprocess the dataset by tokenizing it and removing the stopwords to create a list of terms. Then I calculate the prior probability by dividing the number of documents in each class by the total number of documents. The conditional probability is calcualtes using TF in documents that belong to the class. However, in order to not get 0 in conditional probability we can use Laplace smoothing and use the smoothing parameter a = 1 , we add 1 to every probability, therefore the probability will never be zero.
for prime_genre in categories:
result[prime_genre] = prior[prime_genre]
for term in user_query_terms:
if term in conditionalProb:
result[prime_genre] = result[prime_genre] * conditionalProb[term][prime_genre]
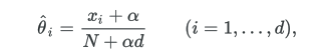
Link to Github
Link to repository on github and Readme instructions on how to run. Github
Challenges faced:
Some of the challenges I faced when developing the classifier was the Dataset I was using, the dataset on kaggle was comprised of two csv’s.One had the textual component which was the description and the other had the primary genre of the app. I tried to to process both CSV’s separately and it was taking significantly long. I had to merge the column of the prime_genre to the main CSV and ran it that way. Also, When I was initially clasifying the dataset contained about 60% of the apps were categorized as “Games” so initially for my results, It was giving a very high classification score to most queries even if is not related to games. I ended up mofifying my dataset by deleting those with “Games” as categories and my classifier began to get better results. This made the size of my dataset to about 3.5K rows. The Dataset has 10+ categories but I only print out the top 4 categories.
Experiments
For my experiments I changed the smoothing parameter and modified it to see what produced the best results. a=0.1, a=10, a=50, a=100. The results were pretty similar but 1 typically worked the best.